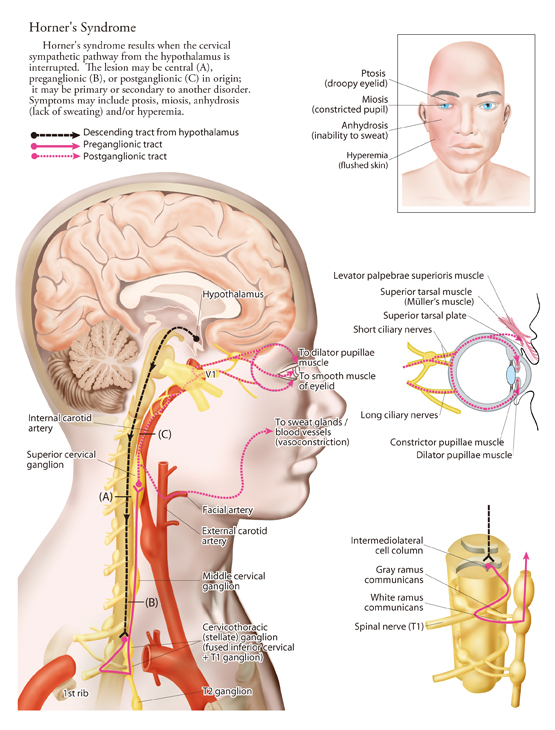
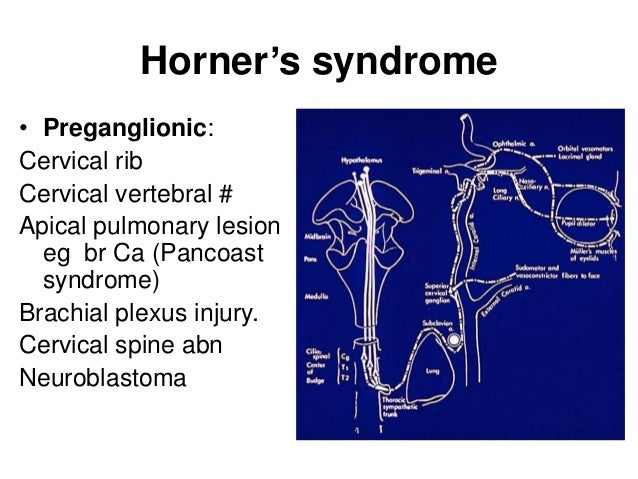
Horner's Syndrome Brachial Plexus
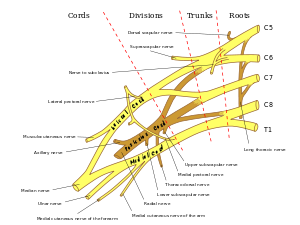
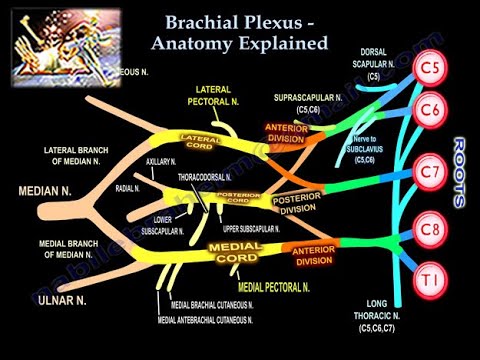
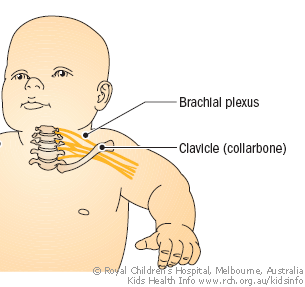
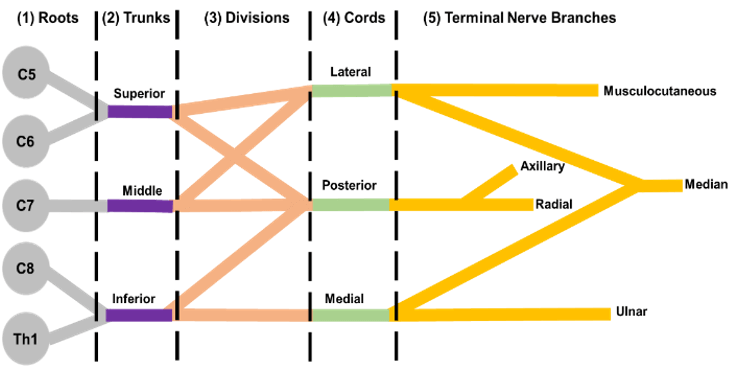
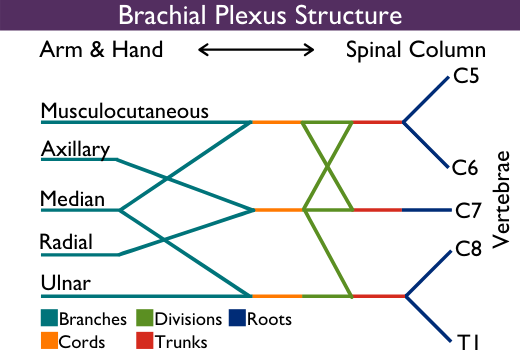
Horner's syndrome brachial plexus. Brachial plexus motor and sensory innervation. Horners syndrome has been reported following several regional anaesthetic techniques including brachial plexus cervical plexus and epidural blocks. Stellate ganglia provide sympathetic fibers to the heart.
560150 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. Horners syndrome the triad of miosis ptosis and enophthalmos is a common complication of regional blockade of the brachial plexus following disruption of sympathetic nerve input from the cervical sympathetic ganglia 1 A. Horners sydrome and ipsilateral brachial plexus block during an epidural analgesia labour procedure.
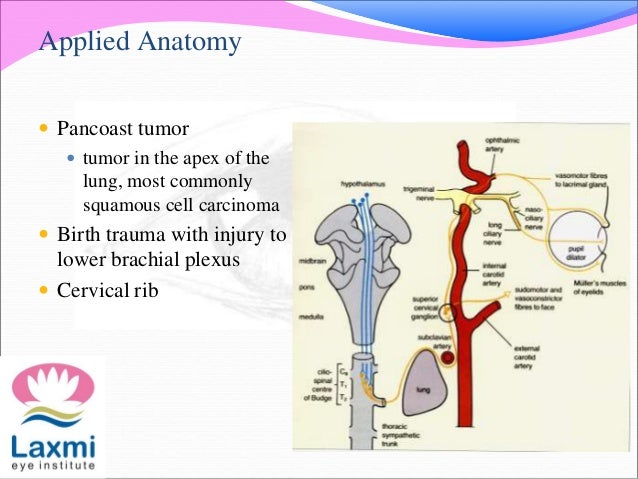
Educational video describing the condition of Horners SyndromeHorners syndrome can occur from an avulsion of the brachial plexus at C8-T1 level. We present the case of a patient who developed Horners syndrome as the first manifestation of neurolymphomatosis NL of the brachial plexus that did not have the usually associated bulky adenopathyPancoast syndrome phenotype. Hoarseness and Horners syndrome after interscalene brachial plexus block.
Horners syndrome is an uncommon side effect after epidural analgesia which occurs more frecuently in pregnant women due to physiological and anatomical changes. It may occur after numerous pathologies in the cervical region epidural spinal anaesthesia and interscalene transscalene supraclavicular or infraclavicular brachial plexus block. However it has a low incidence and the association with ipsilateral bra-.
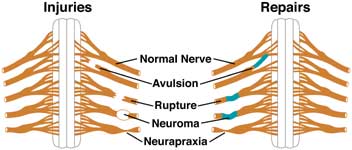
Parsonage-Turner Syndrome PTS also referred to as idiopathic brachial plexopathy or neuralgic amyotrophy is a rare disorder consisting of a complex constellation of symptoms with abrupt onset of pain in the shoulder which is followed by progressive neurologic increasing of motor weakness a reduced sense of touch and numbness. Preganglionic avulsion proximal to dorsal root ganglion. We present a case of Horners Syndrome and complete brachial plexus blockade following epidural bolus of lidocaine for labor analgesia that was initially misdiagnosed as a cerebrovascular accident.
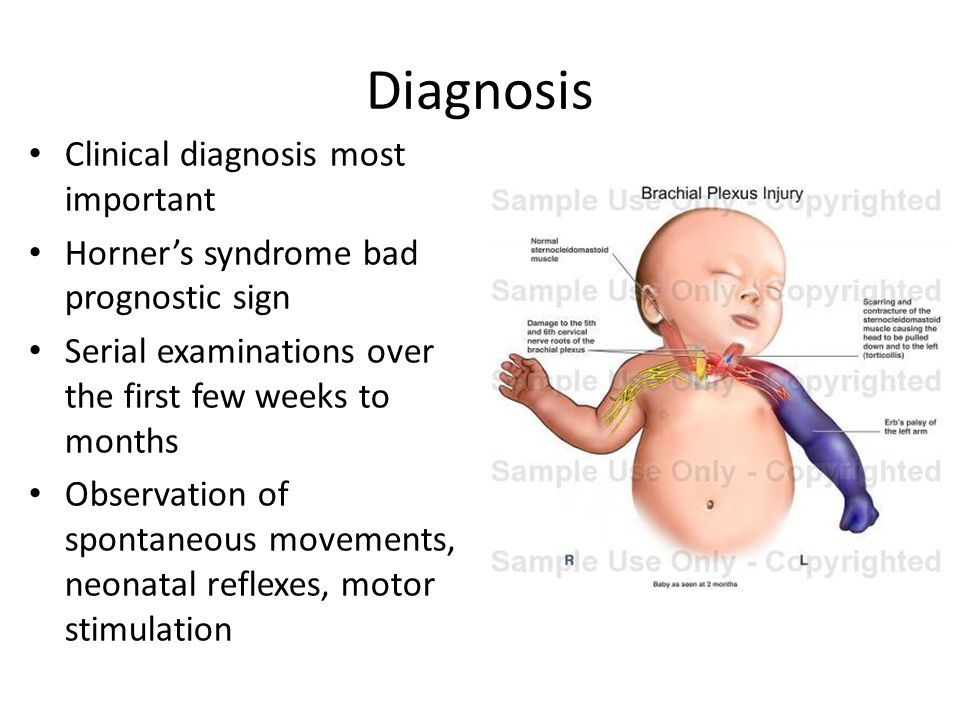
The extent of Horners syndrome can be represented by the difference in pupil diameter between bilateral eyes. In rare cases it has been witnessed after intercostal regional anesthesia. Although Horners syndrome is usually taken as an absolute indicator of avulsions of the C8 and T1 ventral roots in adult brachial plexus injury its pathological basis in obstetric brachial plexus palsy OBPP is unclear.
In rare cases it has been witnessed after intercostal regional anesthesia. SUMMARY Horners syndrome is an uncommon side effect after epi-dural analgesia which occurs more frecuently in pregnant wo-men due to physiological and anatomical changes.
It may occur after numerous pathologies in the cervical region epidural spinal anaesthesia and interscalene transscalene supraclavicular or infraclavicular brachial plexus block.
The extent of Horners syndrome can be represented by the difference in pupil diameter between bilateral eyes. We present the case of a patient who developed Horners syndrome as the first manifestation of neurolymphomatosis NL of the brachial plexus that did not have the usually associated bulky adenopathyPancoast syndrome phenotype. Ipsilateral stellate ganglion block accompanied by interscalene brachial plexus block causes Horners syndrome presenting with miosis ptosis and anhidrosis. Involves CNS which does not regenerate little potential recovery of motor function poor prognosis lesions suggesting preganglionic injury. Horners syndrome the triad of miosis ptosis and enophthalmos is a common complication of regional blockade of the brachial plexus following disruption of sympathetic nerve input from the cervical sympathetic ganglia 1A. Preganglionic avulsion proximal to dorsal root ganglion. In rare cases it has been witnessed after intercostal regional anesthesia. Nerve Blockadverse effects Substances. It may occur after numerous pathologies in the cervical region epidural spinal anaesthesia and interscalene transscalene supraclavicular or infraclavicular brachial plexus block.
Parsonage-Turner Syndrome PTS also referred to as idiopathic brachial plexopathy or neuralgic amyotrophy is a rare disorder consisting of a complex constellation of symptoms with abrupt onset of pain in the shoulder which is followed by progressive neurologic increasing of motor weakness a reduced sense of touch and numbness. Horners sydrome and ipsilateral brachial plexus block during an epidural analgesia labour procedure. It may occur after numerous pathologies in the cervical region epidural spinal anaesthesia and interscalene transscalene supraclavicular or infraclavicular brachial plexus block. Brachial plexus motor and sensory innervation. The extent of Horners syndrome can be represented by the difference in pupil diameter between bilateral eyes. Horner syndrome Horners syndrome is caused by an interruption in the nerve signals that control parts of the face. Horners Syndrome HS with brachial plexus involvement following lumbar epidural anesthesia may be a startling event for the patient and providers.






























Post a Comment for "Horner's Syndrome Brachial Plexus"